Samba не видит сеть Windows
Windows не видит samba в Сетевом окружении
Windows перестала видеть машину с samba, ну то есть в сетевом окружении нет имени машины (звать его SERVER1), а вот так \SERVER1sdb заходит (sdb – это имя шары, конфиг приложу ниже) Собственно вот конфиг, вот вывод testparm, вот тут скриншиншот как ведёт себя винда раз, два. Система Windows 10 1709 (Сборка ОС 16299.125), Ubuntu Server 17.04 samba 4.5.8. И вот что я выполнял на сервере, возможно после этого оно перестало работать sudo smbcontrol smbd close-share sdb,IPC$ , ещё кажется я прибивал процессы samba командой sudo smbcontrol (тут были пиды процессов, бил всех) shutdown Пожалуйста, помогите.


Господи, ну не работает в винде обозреватель компов, никогда нормально не работал и не будет.

Господи, ну не работает в винде обозреватель компов, никогда нормально не работал и не будет.
Я думал в Microsoft работают опытные программисты.

Они тоже так думали. те погроммисты.
что в 7ке нифига по вай-ваю не было видно, что сейчас в 10 с парой виртуалок.
может оно при живом железячном windows server + ad в доменчик логон.. может и видно.
В samba NETBIOS настроен?

Оффтопик же. Предлагаю Вам обратиться с этим вопросом на Винфак.
Если вы используете v1709, то не должно быть проблем с доступом к Samba.
NetBIOS — монструозная часть ужаса, которая, как известно, не работает правильно большую часть времени.
Вы должны убедиться, что клиент Windows находятся в одной рабочей группе. Ваш брандмауэр Windows должен также разрешать трафик через TCP/UDP 137. Если вы открываете Powershell, отображаются ли ваши другие устройства или Windows бросает ошибку?

В samba NETBIOS настроен?
Ну я там smb.conf прилагал к посту. А у NETBIOS отдельный конфиг?

Вы должны убедиться, что клиент Windows находятся в одной рабочей группе. Ваш брандмауэр Windows должен также разрешать трафик через TCP/UDP 137. Если вы открываете Powershell, отображаются ли ваши другие устройства или Windows бросает ошибку?
Windows и samba находятся в одной локальной сети и в одной рабочей группе. 137 порт разрешён. Я написал сюда потому что думал что с samba проблемы, но раз не с ней пойду на Винфак.
Если вы открываете Powershell, отображаются ли ваши другие устройства или Windows бросает ошибку?
В каком смысле? Просто открыть Powershell или выполнить в нём что-то?
Присоединюсь. Да и сама идея не особо пригодная в жизни. Лазить по списку/спискам которые еще имеют свойство тупить при открытии, для сохранения/открытия файла «радости» не доставляет. Один фиг юзверам ярлычки/сетевые диски нужны. А админ наберет \nnnnn.
[РЕШЕНO] SAMBA не видит в ФМ ни каких компьютеров сети ни linux ни windows, изменился протокол добавляем “client max protocol = NT1 в /etc/samba/smb.conf”


vs220
browseable = no на yes
Невозможно найти рабочие группы в вашей локальной сети. Возможно, этому препятствует брандмауэр.
nmbd.service – Samba NetBIOS name server
Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/nmbd.service; enabled; vendor preset: disabled)
Active: active (running) since Sun 2018-02-25 19:48:19 MSK; 2min 18s ago
Process: 7566 ExecStart=/usr/bin/nmbd -D (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
Main PID: 7572 (nmbd)
Tasks: 1 (limit: 4915)
CGroup: /system.slice/nmbd.service
└─7572 /usr/bin/nmbd -D
фев 25 19:48:19 VELES systemd[1]: Starting Samba NetBIOS name server.
фев 25 19:48:19 VELES systemd[1]: Started Samba NetBIOS name server.
фев 25 19:48:19 VELES nmbd[7572]: [2018/02/25 19:48:19.256992, 0] ../lib/util/become_daemon.c:124(daemo
фев 25 19:48:19 VELES nmbd[7572]: STATUS=daemon ‘nmbd’ finished starting up and ready to serve connect
фев 25 19:48:42 VELES nmbd[7572]: [2018/02/25 19:48:42.002949, 0] ../source3/nmbd/nmbd_become_lmb.c:397
фев 25 19:48:42 VELES nmbd[7572]: *****
фев 25 19:48:42 VELES nmbd[7572]:
фев 25 19:48:42 VELES nmbd[7572]: Samba name server VELES is now a local master browser for workgroup
фев 25 19:48:42 VELES nmbd[7572]:
фев 25 19:48:42 VELES nmbd[7572]: *****
● smbd.service – Samba SMB/CIFS server
Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/smbd.service; enabled; vendor preset: disabled)
Active: active (running) since Sun 2018-02-25 19:48:19 MSK; 3min 13s ago
Process: 7574 ExecStart=/usr/bin/smbd -D (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
Main PID: 7575 (smbd)
Tasks: 4 (limit: 4915)
CGroup: /system.slice/smbd.service
├─7575 /usr/bin/smbd -D
├─7579 /usr/bin/smbd -D
├─7580 /usr/bin/smbd -D
└─7581 /usr/bin/smbd -D
фев 25 19:48:19 VELES systemd[1]: Starting Samba SMB/CIFS server.
фев 25 19:48:19 VELES systemd[1]: Started Samba SMB/CIFS server.
фев 25 19:48:19 VELES smbd[7575]: [2018/02/25 19:48:19.325375, 0] ../lib/util/become_daemon.c:124(daemo
фев 25 19:48:19 VELES smbd[7575]: STATUS=daemon ‘smbd’ finished starting up and ready to serve connect
lines 1-16/16 (END)
Рядом на компе стоит ubuntu все работает, как всегда с арчем все перемудрили
Вы вроде на кде перешли не забыли для него настроить
https://wiki.archlinux.org/index.php/Samba#KDE
Нет сейчас самбы проверить.
Запустите авахи с ним проблем нет.
перезагрузите фм должны быть видны компы, если нет то может точно что блочит

vs220
Вы вроде на кде перешли не забыли для него настроить
https://wiki.archlinux.org/index.php/Samba#KDE
Нет сейчас самбы проверить.
Запустите авахи с ним проблем нет.
перезагрузите фм должны быть видны компы, если нет то может точно что блочит
Если честно ничего не понял что там написано вставил строки
server multi channel support = yes
socket options = IPTOS_THROUGHPUT SO_KEEPALIVE
deadtime = 30
use sendfile = Yes
write cache size = 262144
min receivefile size = 16384
aio read size = 16384
aio write size = 16384
nt pipe support = no
load printers = No
printcap name = /dev/null
disable spoolss = Yes
Все перезагрузил результат прежний, avchi тоже запущен и тоже ничего не видит, рядом 2 компа на ubuntu все работает
Блин почему в этой ос все через одно место, за что не возьмись все не работает или работает с такими костылями, ну была нормальная самба сделал все по вики и работает а сейчас
Ради ржаки загрузился с загрузочной флешки линукс минт, самба все видит
Samba не видит сеть Windows Network
![]()
Не видны шары винды на Linux машине.
Linux Mint 15 (впрочем из Live CD Ubuntu тоже же самое, шары винды не видны)
Конфиг самбы:
[code=php][global]
dos charset = CP866
display charset = UTF-8
netbios name = ant
server string =
workgroup = WORKGROUP
interfaces = lo, eth0, wlan0
security = user
null passwords = Yes
username map = /etc/samba/users.map
syslog = 0
log file = /var/log/samba/log.%m
max log size = 1000
lm announce = yes
lm interval = 120
os level = 20
domain master = No
local master = Yes
preferred master = Auto
name resolve order = bcast lmhosts host wins
[homes]
comment = Home Directories
path = /home
valid users = %U
read only = no
available = yes
browseable = yes
writable = yes
guest ok = no
public = no
printable = no
locking = no
strict locking = no[/code]
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Подскажите, пожалуйста, Mint 17.1 Rebecca & Windows 7 – всё х64.
Менеджеры – Nemo, DoubleCommander, Crusader – видят папки Win7 на ДРУГОМ компьютере по сети (LAN).
Но не могу скопировать файлы с папок Windows на папку Windows на другом компе. Постоянно требуют пароль. Пароли root и пароли Windows не прокатывают. Причем. Последний проходит при подключении к домашней группе среди компов с Windows. Если не появляется требование пароля (например, в Nemo, то – “доступ запрещен”. Пробовал установить права доступа на данную папку/диск на другом компе с Windows, но “не удалось определить права доступа”.В чём дело? Спасибо.
PS Если непонятно, то добавлю.
Три компа –
№1 – Mint Rebecca 17.1 x64 & Windows 10 X64
#2 – Windows 7 x86 – файлохранилище.
№3 – windows 7 x86 – ноутбук, подклчен к ТВ для просмотра фильмов.
Всё в сети LAN.
Находясь в linux Mint не могу скопировать файлы с win-папок №1 в win-папку №2.
На самом деле Ubuntu прекрасно работает с Windows сетью и доменами, просто не все об этом знают.
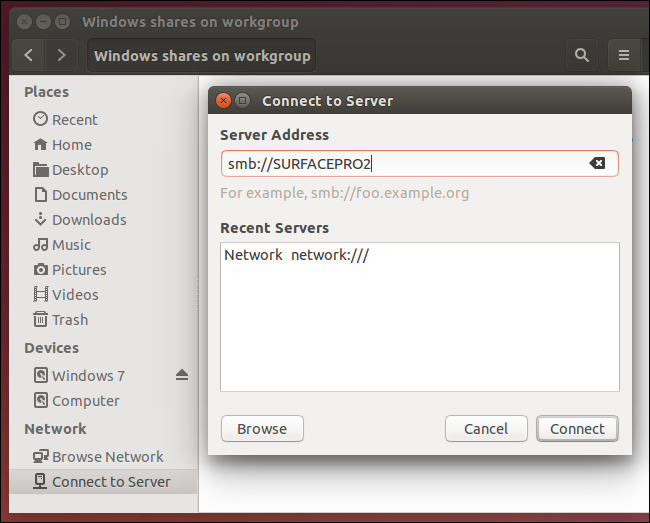
По не совсем понятной мне причине, даже последних версиях Ubuntu по умолчанию нет клиента для работы с Windows сетями – Smb. Не беда открываем терминал: sudo apt-get install samba идём в Other locations и пишем:
smb://”IP или имя Windows системы”/”имя папки”. И ничего не открывается. Оказывается в Samba по умолчанию не включена поддержка smb2 и smb3 протокола необходимого для сетевой авторизации для всего что Windows 7 и выше. Нужно отредактировать файл /etc/samba/smb.conf и включить поддержку. Но вот беда файл защищён системой, поэтому отредактировать то его можно, а вот сохранить нет. Опять открываем терминал и пишем: sudo nano /etc/samba/smb.conf
Вводим пароль администратора и ищем строку: workgroup = WORKGROUP добавляем enter ниже дописываем client min protocol = SMB2 ещё раз enter client max protocol = SMB3. Чтобы в законченом виде выглядело вот так:
client min protocol = SMB2
client max protocol = SMB3
Теперь нажмите ctrl+O чтобы сохранить файл конфигурации и нажмите ещё раз enter.
Последний штрих перезапустить сервис SMB напишите в терминале: service smb start у меня почему-то эта комманда не проходила, поэтому пришлось перезапустить систему.
Теперь идём Files/Other Locations или Connect to Server и пишем: smb://”IP или имя Windows системы”/”имя папки” и вместо ошибки появляется диалог подключения. Тут тоже всё довольно просто.
User: IP или имя Windows системы компьютера к которому вы подключаетесьимя пользователя которому открыт доступ к этой папке. Например Server1User03 если в сети есть домен авторизации пользователей на другой машине и доступ открыт через домен нужно указывать сервер авторизации например USER-AUTHUser03 опять же если система в той же подсети, она сможет видеть сервер авторизации пользователей в домен не заходя. Обратите внимание, пользователь находится на удалённой системе, а не на вашей поэтому пишем Server1User03. (Единственное исключение если и на Windows и на Ubuntu будет создан пользователь User03 с одинаковым паролем, тогда можно Server1 не писать, но так лучше не делать).
Domain: WORKGROUP – Доменное имя можно оставить как есть, если система не входит в домен, открывать расшаренные папки внутри домена это не мешает.
Password: Пароль пользователя User03 на Windows машине которому открыт доступ к папке.
Если всё сделано правильно, то папка откроется. Если всё равно не открывается, проверьте настроки антивируса, Kaspersky например по умолчанию давит запросы Ubuntu системы даже если она находится в доверенной сети. Надеюсь пост поможет людям которые хотят использовать свою Ubuntu например на рабочем месте, а Windows заточенные админы только разводят руками и говорят “Ну это же Ubuntu, мы тут не знаем”. Достойное место в домашней сети Ubuntu тоже может прекрасно занять особенно на более старом железе, которое медленно тянет Win10. Не могу сказать, что я в восторге от всех этих плясок с терминалом, но в целом очень достойная и главная абсолютно бесплатная ОС.
Samba не видит сеть Windows
20 май 2019, 13:18
System: Host: juss1962-GS Kernel: 4.15.0-50-generic x86_64
bits: 64 gcc: 7.3.0
Desktop: Cinnamon 3.8.9 (Gtk 3.22.30-1ubuntu3)
Distro: Linux Mint 19 Tara
Machine: Device: desktop Mobo: ASUSTeK model: A68HM-K v: Rev X.0x serial: N/A
UEFI: American Megatrends v: 1301 date: 11/03/2015
CPU: Quad core AMD Athlon X4 840 (-MCP-)
arch: Steamroller rev.1 cache: 8192 KB
flags: (lm nx sse sse2 sse3 sse4_1 sse4_2 sse4a ssse3 svm) bmips: 24739
clock speeds: max: 3100 MHz 1: 1396 MHz 2: 1395 MHz 3: 3784 MHz
4: 3770 MHz
Graphics: Card: NVIDIA G92 [GeForce 9800 GT] bus-ID: 01:00.0
Display Server: x11 (X.Org 1.19.6 )
drivers: nouveau (unloaded: modesetting,fbdev,vesa)
Resolution: 1680×1050@59.88hz, 1920×1080@60.00hz
OpenGL: renderer: NV92 version: 3.3 Mesa 18.2.8 Direct Render: Yes
Audio: Card Advanced Micro Devices [AMD] FCH Azalia Controller
driver: snd_hda_intel bus-ID: 00:14.2
Sound: Advanced Linux Sound Architecture v: k4.15.0-50-generic
Network: Card: Realtek RTL8111/8168/8411 PCIE Gigabit Ethernet Controller
driver: r8169 v: 2.3LK-NAPI port: d000 bus-ID: 04:00.0
IF: enp4s0 state: up speed: 1000 Mbps duplex: full mac:
Drives: HDD Total Size: 1000.2GB (7.5% used)
ID-1: /dev/sda model: ST1000DM003 size: 1000.2GB
Partition: ID-1: / size: 917G used: 70G (9%) fs: ext4 dev: /dev/sda5
RAID: No RAID devices: /proc/mdstat, md_mod kernel module present
Sensors: System Temperatures: cpu: 22.0C mobo: N/A gpu: 55.0
Fan Speeds (in rpm): cpu: 0
Info: Processes: 238 Uptime: 23 min Memory: 3850.5/7920.8MB
Init: systemd runlevel: 5 Gcc sys: 7.4.0
Client: Shell (bash 4.4.191) inxi: 2.3.56
Всё починил. Нашёл вот эту ссылку https://www.linuxmint.com.ru/viewtopic.php?t=3185
Однако странно то, что реально обновлений не устанавливалось, а получается что samba сама обновилась?
Всем, кто пытался помогать, огромное спасибо за потраченное время!
![]()
Samba перестала видеть локальную сеть
20 май 2019, 13:29
![]()
Samba перестала видеть локальную сеть
20 май 2019, 13:32
# Change this to the workgroup/NT-domain name your Samba server will part of
workgroup = UNIGRIND
# server string is the equivalent of the NT Description field
server string = %h server (Samba, Ubuntu)
# Windows Internet Name Serving Support Section:
# WINS Support – Tells the NMBD component of Samba to enable its WINS Server
# wins support = no
# WINS Server – Tells the NMBD components of Samba to be a WINS Client
# Note: Samba can be either a WINS Server, or a WINS Client, but NOT both
; wins server = w.x.y.z
# This will prevent nmbd to search for NetBIOS names through DNS.
dns proxy = no
# The specific set of interfaces / networks to bind to
# This can be either the interface name or an IP address/netmask;
# interface names are normally preferred
; interfaces = 127.0.0.0/8 eth0
# Only bind to the named interfaces and/or networks; you must use the
# ‘interfaces’ option above to use this.
# It is recommended that you enable this feature if your Samba machine is
# not protected by a firewall or is a firewall itself. However, this
# option cannot handle dynamic or non-broadcast interfaces correctly.
; bind interfaces only = yes
# This tells Samba to use a separate log file for each machine
# that connects
log file = /var/log/samba/log.%m
# Cap the size of the individual log files (in KiB).
max log size = 1000
# If you want Samba to only log through syslog then set the following
# parameter to ‘yes’.
# syslog only = no
# We want Samba to log a minimum amount of information to syslog. Everything
# should go to /var/log/samba/log.
# through syslog you should set the following parameter to something higher.
syslog = 0
# Do something sensible when Samba crashes: mail the admin a backtrace
panic action = /usr/share/samba/panic-action %d
# Server role. Defines in which mode Samba will operate. Possible
# values are “standalone server”, “member server”, “classic primary
# domain controller”, “classic backup domain controller”, “active
# directory domain controller”.
#
# Most people will want “standalone sever” or “member server”.
# Running as “active directory domain controller” will require first
# running “samba-tool domain provision” to wipe databases and create a
# new domain.
server role = standalone server
# If you are using encrypted passwords, Samba will need to know what
# password database type you are using.
passdb backend = tdbsam
obey pam restrictions = yes
# This boolean parameter controls whether Samba attempts to sync the Unix
# password with the SMB password when the encrypted SMB password in the
# passdb is changed.
unix password sync = yes
# For Unix password sync to work on a Debian GNU/Linux system, the following
# parameters must be set (thanks to Ian Kahan for
# sending the correct chat script for the passwd program in Debian Sarge).
passwd program = /usr/bin/passwd %u
passwd chat = *Entersnews*spassword:* %nn *Retypesnews*spassword:* %nn *passwordsupdatedssuccessfully* .
# This boolean controls whether PAM will be used for password changes
# when requested by an SMB client instead of the program listed in
# ‘passwd program’. The default is ‘no’.
pam password change = yes
# This option controls how unsuccessful authentication attempts are mapped
# to anonymous connections
map to guest = bad user
#
# The following settings only takes effect if ‘server role = primary
# classic domain controller’, ‘server role = backup domain controller’
# or ‘domain logons’ is set
#
# It specifies the location of the user’s
# profile directory from the client point of view) The following
# required a [profiles] share to be setup on the samba server (see
# below)
; logon path = \%Nprofiles%U
# Another common choice is storing the profile in the user’s home directory
# (this is Samba’s default)
# logon path = \%N%Uprofile
# The following setting only takes effect if ‘domain logons’ is set
# It specifies the location of a user’s home directory (from the client
# point of view)
; logon drive = H:
# logon home = \%N%U
# The following setting only takes effect if ‘domain logons’ is set
# It specifies the script to run during logon. The script must be stored
# in the [netlogon] share
# NOTE: Must be store in ‘DOS’ file format convention
; logon script = logon.cmd
# This allows Unix users to be created on the domain controller via the SAMR
# RPC pipe. The example command creates a user account with a disabled Unix
# password; please adapt to your needs
; add user script = /usr/sbin/adduser –quiet –disabled-password –gecos “” %u
# This allows machine accounts to be created on the domain controller via the
# SAMR RPC pipe.
# The following assumes a “machines” group exists on the system
; add machine script = /usr/sbin/useradd -g machines -c “%u machine account” -d /var/lib/samba -s /bin/false %u
# This allows Unix groups to be created on the domain controller via the SAMR
# RPC pipe.
; add group script = /usr/sbin/addgroup –force-badname %g
# Using the following line enables you to customise your configuration
# on a per machine basis. The %m gets replaced with the netbios name
# of the machine that is connecting
; include = /home/samba/etc/smb.conf.%m
# Some defaults for winbind (make sure you’re not using the ranges
# for something else.)
; idmap uid = 10000-20000
; idmap gid = 10000-20000
; template shell = /bin/bash
# Setup usershare options to enable non-root users to share folders
# with the net usershare command.
# Maximum number of usershare. 0 (default) means that usershare is disabled.
; usershare max shares = 100
# Allow users who’ve been granted usershare privileges to create
# public shares, not just authenticated ones
usershare allow guests = yes
# Un-comment the following (and tweak the other settings below to suit)
# to enable the default home directory shares. This will share each
# user’s home directory as \serverusername
;[homes]
; comment = Home Directories
; browseable = no
# By default, the home directories are exported read-only. Change the
# next parameter to ‘no’ if you want to be able to write to them.
; read only = yes
# File creation mask is set to 0700 for security reasons. If you want to
# create files with group=rw permissions, set next parameter to 0775.
; create mask = 0700
# Directory creation mask is set to 0700 for security reasons. If you want to
# create dirs. with group=rw permissions, set next parameter to 0775.
; directory mask = 0700
# By default, \serverusername shares can be connected to by anyone
# with access to the samba server.
# Un-comment the following parameter to make sure that only “username”
# can connect to \serverusername
# This might need tweaking when using external authentication schemes
; valid users = %S
# Un-comment the following and create the netlogon directory for Domain Logons
# (you need to configure Samba to act as a domain controller too.)
;[netlogon]
; comment = Network Logon Service
; path = /home/samba/netlogon
; guest ok = yes
; read only = yes
# Un-comment the following and create the profiles directory to store
# users profiles (see the “logon path” option above)
# (you need to configure Samba to act as a domain controller too.)
# The path below should be writable by all users so that their
# profile directory may be created the first time they log on
;[profiles]
; comment = Users profiles
; path = /home/samba/profiles
; guest ok = no
; browseable = no
; create mask = 0600
; directory mask = 0700
[printers]
comment = All Printers
browseable = no
path = /var/spool/samba
printable = yes
guest ok = no
read only = yes
create mask = 0700
# Windows clients look for this share name as a source of downloadable
# printer drivers
[print$]
comment = Printer Drivers
path = /var/lib/samba/printers
browseable = yes
read only = yes
guest ok = no
# Uncomment to allow remote administration of Windows print drivers.
# You may need to replace ‘lpadmin’ with the name of the group your
# admin users are members of.
# Please note that you also need to set appropriate Unix permissions
# to the drivers directory for these users to have write rights in it
; write list = root, @lpadmin
Samba не видит сеть Windows
цитата: Cregg:
“Не удается разрешить системное имя узла CENTOS”
по IP иили FQDN доступ есть? Спасибо.
Дело оказалось в конфиге Samba.
После удаления из конфига всех строк связанных с аудитом (vfs) доступ заработал.
Т.е. конфиг который прекрасно работал в 3-й версии Samba – в 4-й версии не работает.
В /var/log/samba обнаружилась ошибка:
[2017/05/09 17:02:36.193051, 0] ../lib/util/modules.c:48(load_module) Error loading module ‘/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/samba/vfs/full_audit.so’: /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/samba/vfs/full_audit.so: невозможно открыть разделяемый объектный файл: Нет такого файла или каталога
[2017/05/09 17:02:36.193147, 0] ../source3/smbd/vfs.c:184(vfs_init_custom) error probing vfs module ‘full_audit’: NT_STATUS_UNSUCCESSFUL [2017/05/09 17:02:36.193194, 0] ../source3/smbd/vfs.c:349(smbd_vfs_init) smbd_vfs_init: vfs_init_custom failed for full_audit
[2017/05/09 17:02:36.193247, 0] ../source3/smbd/service.c:552(make_connection_snum) vfs_init failed for service IPC$
[2017/05/09 17:02:38.592747, 0] ../lib/util/modules.c:48(load_module) Error loading module ‘/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/samba/vfs/full_audit.so’: /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/samba/vfs/full_audit.so: невозможно открыть разделяемый объектный файл: Нет такого файла или каталога
[2017/05/09 17:02:38.592853, 0] ../source3/smbd/vfs.c:184(vfs_init_custom) error probing vfs module ‘full_audit’: NT_STATUS_UNSUCCESSFUL [2017/05/09 17:02:38.592920, 0] ../source3/smbd/vfs.c:349(smbd_vfs_init) smbd_vfs_init: vfs_init_custom failed for full_audit
[2017/05/09 17:02:38.592972, 0] ../source3/smbd/service.c:552(make_connection_snum) vfs_init failed for service IPC$
[2017/05/09 17:02:51.172312, 1] ../source3/smbd/process.c:554(receive_smb_talloc) receive_smb_raw_talloc failed for client ipv4:192.168.0.47:58714 read error = NT_STATUS_CONNECTION_RESET.
С таким крайне простым конфигом все работает::[global]
workgroup = WORKGROUP2
netbios name = MINT
#server string = %h
interfaces lo, enp4s0
local master = No load printers = No
map to guest = Bad user security = user
unix charset = utf8
browseable = Yes
hosts allow = 127. 192.168.0.
create mask = 777
directory mask = 777
log file = /var/log/samba/log.%m
[1C] path = /mnt/1c
readonly = No
guest ok = No browseable = Yes
[Public] path = /mnt/win/public
readonly = No
Остается вопрос, как все-таки настроить аудит и корзину в 4-й версии Samba?
Вот та часть конфига которая была “выпилена”:: vfs object = recycle full_audit
log level = 1 vfs:1
log file = /var/log/samba/log.%m
full_audit: prefix = %u|%I
full_audit:success = rmdir, unlink, write, rename
full_audit:failure = rmdir, unlink, write, rename
recycle:keeptree = Yes
recycle:touch = Yes
recycle:touch_mtime = Yes
recycle:versions = Yes
recycle:maxsize = 105057800
recycle:exclude = *.iso, *.tmp, *.temp, ?



